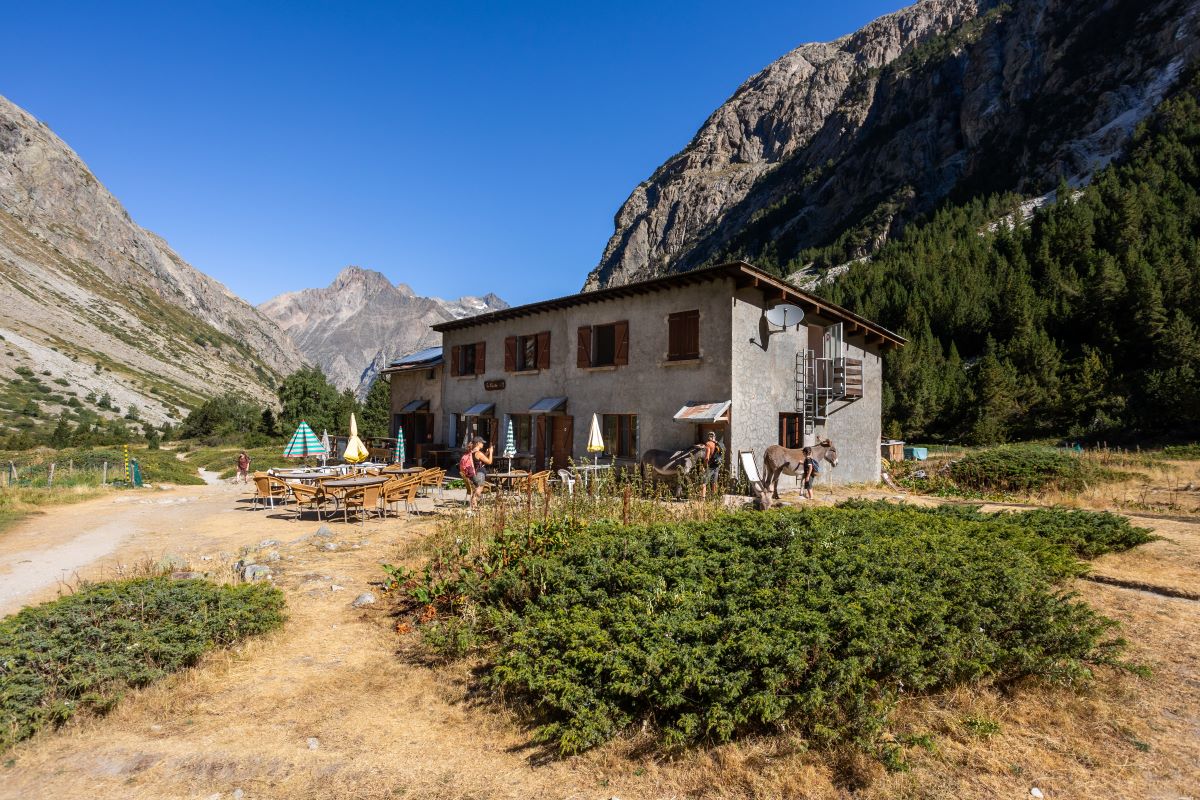

Carrelet Refuge
At the bottom of a rocky valley, the track goes up to the source of the Vénéon and comes out on the Carrelet plain... The verdure of this "plain «contrasts with the abrupt clefts of the Ailefroide which dominate the refuge with a drop of 2000 m. The track has been subject to a lot of restoration work by the teams in the National Park national to make it accessible and pleasurable for hikers.
Description
Either take the path at the bottom of the car park on the edge of the Vénéon torrent or in the village passing the Maison de la Montagne... The itinerary follows the right bank of the Vénéon crossing several secondary torrents equipped with walkways in order to reach Carrelet refuge. The installation of a stone pavement on parts of the track has enabled us to fight against erosion linked to hikers crossing the stream. Return by using the same itinerary.
- Departure : La Bérarde, Saint-Christophe-en-Oisans
- Towns crossed : Saint-Christophe-en-Oisans
15 points of interest

La Bérarde - Hôtel de la Bérarde - Collection PNE  History
HistoryBérarde Hamlet
La Bérarde, is a hamlet representing the history of mountaineering and its corollary touristic development in the vallies. A heterogenous collection of welcoming buildings and businesses. So many modest but representative examples of the successive periods in time of tourist facilities on this emblematic site in the history of this valley.

La Bérarde en Oisans et la vallée de la Pilatte, Laurent Guétal - © Musée de Grenoble  History
HistoryLa Bérarde en Oisans, Laurent Guétal
From the village of La Bérarde, you can go all the way up the River Vénéon as far as the Pilatte refuge. This is probably the route that inspired Laurent Guétal (1841-1892) in his painting La Bérarde in Oisans and the Pilatte Valley. From his forties, the artist travelled all over the Chartreuse, Belledone and Oisans. Considered one of the major painters of the Dauphiné landscape in the second half of the 19th century, he transmitted his passion for the mountains to a large number of pupils, in particular Edouard Brun and Charles Bertier.
Trèfles saxatile - PNE - Nicolas Marie-Geneviève  Flora
FloraRock Clover
This small rare clover colonizes the moraines and the crystalline gravel like that at the confluence of the Vénéon with the Romanche up to the Chardon valley. With a whitish colour or pinkish its flowers are small and have white hairs that gives them a fluffy appearance.

 Know-how
Know-howModification work around the trails
In La Bérarde area, some trails are very popular. The presence of hikers, as well as sometimes intense natural erosion, has led to work being carried out by technicians from the national park. There are several kinds of renovation work : channels allowing the water on the slopes to be evacuated and prevent the trail from turning into a mountain stream, steps or paving to protect the ground from rapid erosion by rain and making progress easier for hikers, and low supporting walls. All the renovation work is carried out using materials found onsite and respecting traditional methods.

Automne en Oisans, la Bérarde - Thierry Maillet - Parc national des Ecrins  History
HistoryThe beginning of the National Park in 1913
At the beginning of the 20th century, the need to protect the slopes of the high mountain at Haut Vénéon emerged in order to limit the erosion of the ground and the torrential flooding that the Omanche and its affluent the Vénéon were subjected to. Deforestation and pastoral exploitation were blamed at that time. So in 1913, after long negotiations the State bought around 4000 hectares of ground from the commune of Saint-Christophe-en-Oisans to make a « National Park ». The development of tourism and mountaineering spearheaded by the CAF and the Touring Club of France from the second half of the 19th century in the sector of Oisans was not unconnected from this either. The Inspector for Waters and Forests wrote that the creation of a Park would involve « advantages for the commune of Saint-Christophe as well as for the development of tourism in the Dauphiné ». This innovative Park, at that time, was not drawn up in relation to any written law or regulatory framework resulting in several vague points like the different denominations used (Bérarde, Oisans, Pelvoux, etc.).

 History
HistoryExtension of the limits of the first «National Park»
It has been evoked that the park was known locally as the "Parc de la Bérarde". The Administration sometimes employed the denomination "National Park of Oisans" until the acquisition new plots at Pelvoux in 1923 (Celse-Nière valley, the black glacier, the white glacier). The appellation of the Park now concerning the different slopes of the Pelvoux massif became henceforth the « Pelvoux National Park». The extension of the Park to the territory of Valgaudemar carried out in 1924, brought the whole surface area of the park to 13 000 ha. In 1955, A national hunting reservation was created on the perimeter of the Pelvoux National Park. Despite the action of the foresters after the war it was not a favourable period for the Pelvoux National Park which experienced limitations: a small amount of financial credit, the absence of a managerial structure and practically inexistent scientific studies. The "Ecrins National Park" saw the light of day on the 27th March 1973 within the framework of the law of 1960, which created a real status for the French National Parks.

 History
HistorySupervision, knowledge and layout Bérarde Park
The conservationist at Waters and Forests in Gap was concerned about supervision at the Park and suggested that land-guides be recruited like auxiliary-guards. « These experienced mountaineers would help to supervise hunting, The Park must be a first rate reserve of chamois, they should help the forestry service in the studies and the work to be carried out in the Park. ». Two positions were created in 1927. In 1910, the request made to the Italian administration concerning the re-introduction of Alpine Ibex came to nothing. In 1913, an authorization for the transport of Wood Grouse from Belgium was issued without anybody knowing whether or not the birds were actually released on the massif.

La route de la Bérarde - PNE - Collection Tron Lucien  History
HistoryPioritizing nature
In the first years, the principal of letting nature to itself prevailed concerning requests to the reafforestation of Larch and Swiss pines in certain forests. In spite of everything after the second world war the terrains would be restored by the reafforestation of the Park and its close periphery. The presence of visitors had never been excluded and the Forestry Administration which carried out arrangements for tourists... It was mainly structures linked to mountaineering like the opening of restoration of the tracks like those enabling access to the refuges at Temple-Ecrins, the Pillate and Gioberney. Grants were also awarded for the construction of refuges. The Ailefroide route to Pré de Madame Carle was also opened in 1937-1938 for touristic purposes.

La Vallée de la Pilatte, Laurent Guétal - © Musée de Grenoble  History
HistoryThe Pilatte Valley, Laurent Guétal
Laurent Guétal began painting natural scenes at an early age, but only began painting the mountains in the last few years of his life, creating the works that made him famous. Among them are Lake Eychauda (1886), the Entraigues Valley (1887) and the Pilatte Valley, a painting that was exhibited at the Paris Salon in 1888. He was the first artist to show the real face of the Dauphiné Alps, a mountain range that was still little known at the time.
Le plan du Carrelet et l'Ailefroide - Cyril Coursier - Parc national des Ecrins  History
HistoryThe creation of the Ecrins National Park
Lucien Devies, president of the Fédération Française de la Montagne and former President of CAF wrote a plea in the December 1963 issue of the CAF review for the creation of a « National Park in the Haut Dauphiné » on the perimeter of the Ecrins massif. The State Administration then took over. However, the project for a National Park in the Pyrénées was keeping the agents occupied. They had to wait until 1969 and a new intervention by Lucien Devis (still by way of the CAF review) for the project to be launched. A fact finding mission was given to Florent in 1971. After several phases of consultation and concertation with local politicians , le decree for the creation of the «Ecrins National Park » was signed on the 27th March 1973 over a protected surface of 91 800 ha. Making it the fifth National Park officially created. Others would follow; in 2013, France can count 10 National Parks...

Le Vénéon à la Bérarde - PNE - Roche Daniel  Water
WaterHaut Vénéon
It’s in this valley that the Vénéon torrent has its source which gives its name to the valley. In the Autumn , then in Winter and Spring, the waters of the Vénéon have a remarkable colour depending on the light of the day... This particular shade can be explained by the strong mineralization which saturates the water and reflects the sun’s rays. In fact, under the action of the melting snow, the water runs in all directions and washes fine particles of silica more or less coloured and partially dissolved. You just have to collect some water, let it evaporate to see the very finely textured deposit: rock flour.

Azuré du serpolet - PNE - Grosselet Olivier  Fauna
FaunaLarge Blue Butterfly
This butterfly with blue wings spotted with black frequents the mountain grasslands and entrusts the ants with rearing its caterpillars... It lays its eggs on the host plant, the Breckland Thyme, whose flower buds feed the caterpillar until it lets itself fall to the ground. The Fire Ants take over. They are attracted by the honeydew produced by the caterpillar and they transport it to their anthill to milk it. . The caterpillar becomes carnivorous and eats the young ant larvae without being disturbed. It hibernates until the Spring. When it reaches maturity, it creates a chrysalis in the anthill. The butterfly hatches and quickly goes out in to the open air to carry out the reproduction of the species.

Versant nord ouest d'Ailefroide - PNE - Roche Daniel  Panorama
PanoramaConquest of the Ailefroide
By its magnitude, its height, its steepness, the conquest of the North-West face of the Ailefroide (impressive view of the North-West face of the Ailefroide which dominates Carrelet plain at an altitude of 3954 m) it is comparable with the famous Northern face of the Grandes Jorasses by Devies. The first ascent carried out by the corded team Devies and Gervasutti on the 23rd and 24th July 1936. On the approach from the Temple-Ecrins refuge Gervasutti broke a rib which did not stop him from carrying out this prestigious first.

Pin à crochet (arbre de droite) - PNE - Nicollet Bernard  Flora
FloraMountain Pine pinewood
The pinewood of Mountain Pines at Carrelet is rightly considered to be the highest in Europe. In fact, it occupies a slope at an altitude of 2400 m. It is also developing downwards due to the end of pastoral bovine activity at the beginning of the 1970s. Progressively, the grassland has been colonized by the juniper heath which encourages the implantation of Mountain Pine.
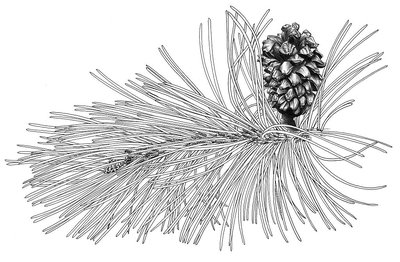
Pin à crochets - PNE - Lévy Frédérique  Flora
FloraMountain Pine
The Mountain Pine is a high altitude species. This tree can be seen on the sunny slopes up to an altitude of 2450 m. If it can reach a height of 15 m locally it becomes much shorter and crooked even bushy when conditions are difficult... Its roots are solid, it is a frugal species that can support a very short vegetative period, extreme cold, snow, drought, the alpine brightness, the wind and the black ice,. It can be used as a species for reafforestation at altitude with a view to protecting certain soils and to fight against the beginning of avalanches...
Forecast
Altimetric profile
Sensitive areas
Golden eagle
- Impacted practices:
- Aerial, , Vertical
- Sensitivity periods:
- JanFebMarAprMayJunJulAug
- Contact:
- Parc National des Écrins
Julien Charron
julien.charron@ecrins-parcnational.fr
Golden eagle
- Impacted practices:
- Aerial, , Vertical
- Sensitivity periods:
- JanFebMarAprMayJunJulAug
- Contact:
- Parc National des Écrins
Julien Charron
julien.charron@ecrins-parcnational.fr
Information desks
Oisans Park house
45 avenue de la République, 38520 Le Bourg d'Oisans
Video presentation of the natural resources of the Oisans mountain and its crafts. Information, documentation about the Park, projections, reading space for children. Accessible to people with reduced mobility. Free admission. All animations of the Park are free unless otherwise stated.
Transport
Coach stop : La Bérarde
Access and parking
From Bourg d'Oisans, take the D1091 then the D530 in the direction of Bérarde (34 km). Narrow road from Champhorent, closed in Winter.
Parking :
More information
Source

Report a problem or an error
If you have found an error on this page or if you have noticed any problems during your hike, please report them to us here:


